How Does a Vortex Flow Meter Work?

Vortex flow meters operate according to the principle of the Kármán vortex street. The Kármán vortex street is a phenomenon in fluid mechanics, in which opposite vortices are formed behind a bluff body.
The bluff body and the sensor of the electronics are located inside the measuring pipe. When the flow impinges on the bluff body, opposite vortices are formed which are offset relative to one another. Thus, a vortex street forms in the flow. This effect is used for flow measurement.

The vortices offset in opposite directions and relative to one another cause local pressure differences which are detected by the sensor as pressure pulses. The pressure pulses are evaluated by the electronics and converted into the output signal of the vortex flow meter. The measured frequency of the signal corresponds to the current flow rate in the measuring pipe.
The measuring principle of the vortex flow meters has the following advantages:
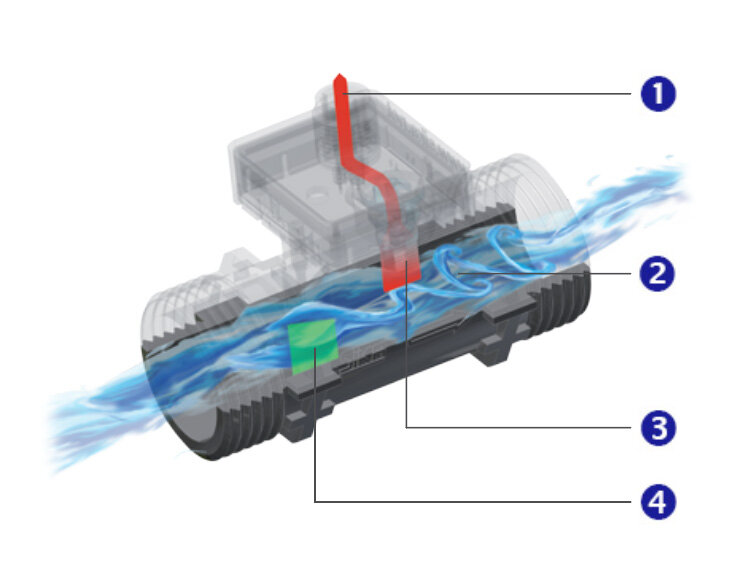
➊ Output signal
➋ Vortex street
➌ Sensor
➍ Bluff body